Invalid Server Certificate In Google Chrome
Feb 12, 2015 The System Time is not the real-time. The SSL certificate has Expired. Google Chrome is not updated. The SSL certificate is not Installed properly. The SSL certificate is not issued by a Trusted Certificate Authority (CA) or a self-signed certificate is used to secure a website. The website is secured with an outdated 128-bit SSL. FIX Your Connection is not Private net errcertauthorityinvalid 2019 100% Work Google Chrome - Duration: 3:26. Processing Brains 63,237 views. Chrome Invalid Server Certificate. The language is only used if Google Chrome; supports it, otherwise it falls back to the user-selected language (or; the local system language). If 'true', you won't be able to change the; language within Google Chrome when launched from PAM since PAM will override; it.

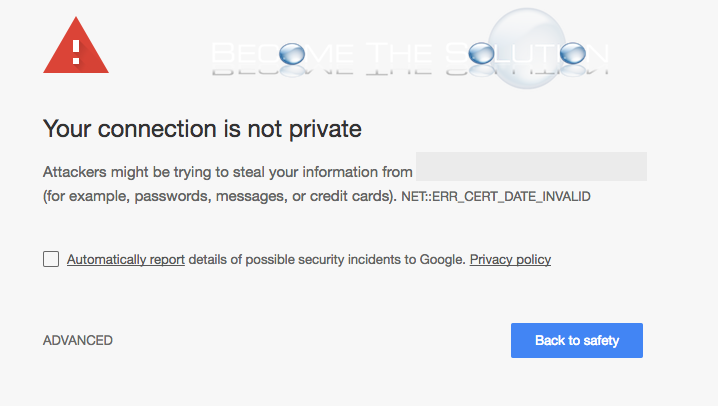
Image: iStock/SergeiKorolkoBrowser manufacturers are always releasing updates intended to improve usability and security. Most changes are benign but some can produce havoc, even if well-intentioned (like blocking java applets when accessing critical internal sites).The latest version of Google Chrome (58), released on April 20, includes a new checking mechanism for secured websites (which are accessed using https). This check analyzes the SSL certificate used by the site to encrypt traffic, and will produce a warning if the certificate does not include the common name of the website (e.g.
Website.company.com) as a subjective alternative name (SAN), which is a fancy word for alias. This check can be suppressed on Windows systems (for a temporary basis at least), and I'll explain how to do so below.The warning appears as follows.
More about cybersecurity.What is a subject alternative name?As I said, a subjective alternative name (SAN) is like an alias which can permit the use of multiple server or host names by a single certificate. Let's say you have a website with a common name of website.company.com.
The website can direct traffic to one of two sites you run; a primary site in Boston (boston.company.com) and a secondary site in Los Angeles (la.company.com).You'd like each site to be able to handle traffic if the other one is unavailable, so you issue an SSL certificate for company.com with two SANs: boston.company.com and la.company.com.In this scenario, however, Chrome will issue the above error if your SSL certificate doesn't include a SAN of website.company.com as that is the common name to which you are connecting.Why did Google make this change?At first glance this may seem illogical. If Google is trying to protect users against spoofed websites, couldn't malicious website operators just add the common name as a SAN and circumvent the issue?Well, they could, but in this case it's not going to work. In the first place, they can't add someone else's common name to their certificate because no public certificate authority will allow that.
Invalid Server Certificate In Google Chrome Browser
Chrome 58 doesn't even check the common name of the site when accessing it, but focuses exclusively on the certificate by looking at the ASCII code involved and not the actual characters.You see, different character sets in different languages can appear similar but are actually viewed as separate entities by a computer. This can allow fake domains to be registered using another name or set of characters to fool visitors.
Chrome 58 mitigates this issue by requiring a SAN matching the common name, which won't match those look alike characters.How can this be resolved?For a single user this is probably a manageable, but annoying, issue. Once I proceeded to a site I did not get the prompt again, although I saw a red security warning associated with the certificate when I returned to the site.For an entire company, however, a fix should be put in place or else the IT department is going to get a LOT of calls (which is probably better than users blithely ignoring security warnings, if you think about it logically).If you're a system administrator, you could always downgrade Chrome installations, but I don't recommend it. You will miss out on other security upgrades down the line. If you're getting this error when accessing internal sites, the best bet is to roll up your sleeves and update the SSL certificates for those sites to include the common name of the website as a SAN.You can buy yourself some time with Windows systems, at least. It's possible to implement or deploy a registry key to suppress this prompt (make sure you know what you're doing when editing a system registry!)Run regedit and access this registry key:HKEYLOCALMACHINESoftwarePoliciesGoogleChromeCreate a REGDWORD subkey called EnableCommonNameFallbackForLocalAnchors and give it a value of 1. Image: Scott Matteson/TechRepublicDouble-clicking this file and answering yes will automatically add this information into the system registry.
It's a bad idea to send such a file to users to ask them to run it (Outlook will likely block it anyhow) so push this out via Active Directory Group Policy, enact the setting via SCCM (if applicable) or arrange a script to install this. Please note it's necessary to restart Chrome for this change to take effect.However, this fix will only remain valid through version 65 of Chrome, so you should still plan to update any SSL certificates you have administrative authority over.Security controls of this nature can generate confusion and frustration, but it's important to keep in mind that for the most part they are well-thought-out and necessary. Google's intention here is to protect users, but probably some sort of advanced warning (such as a message prompt in Chrome 57 that Chrome 58 would include this feature) would make sense next time.
Chrome Says Certificate Is Invalid
Step by step Fixing SSL Certificate Error for “ERRSSLPROTOCOLERROR” in Google ChromeGoogle Chrome, an advanced web browser developed by Google in Sep-2008, is today the world’s most secure web browser & covers market shares of 48.26% of desktop users & 36.29% of mobile users. Google Chrome offers speed, security, and privacy to their users.SSL Certificates are used to secure communication between a client (browser) and a server. About Mit GajjarI have been working as SSL security expert for 6 years and i have assisted to plenty of users to solve their technical issues while installation of SSL certificates on their web servers. It’s really great experience working with Platinum Partner Company CheapSSLSecurity to offer the most reliable SSL certificate security solution on the internet. Being Platinum Partner Company of Symantec, GeoTrust Thawte, Comodo, and RapidSSL, CheapSSLSecurity offers the cheapest SSL certificates security on the internet which starts at just only $3.20/yr.